Understanding the difference between Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) vs. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
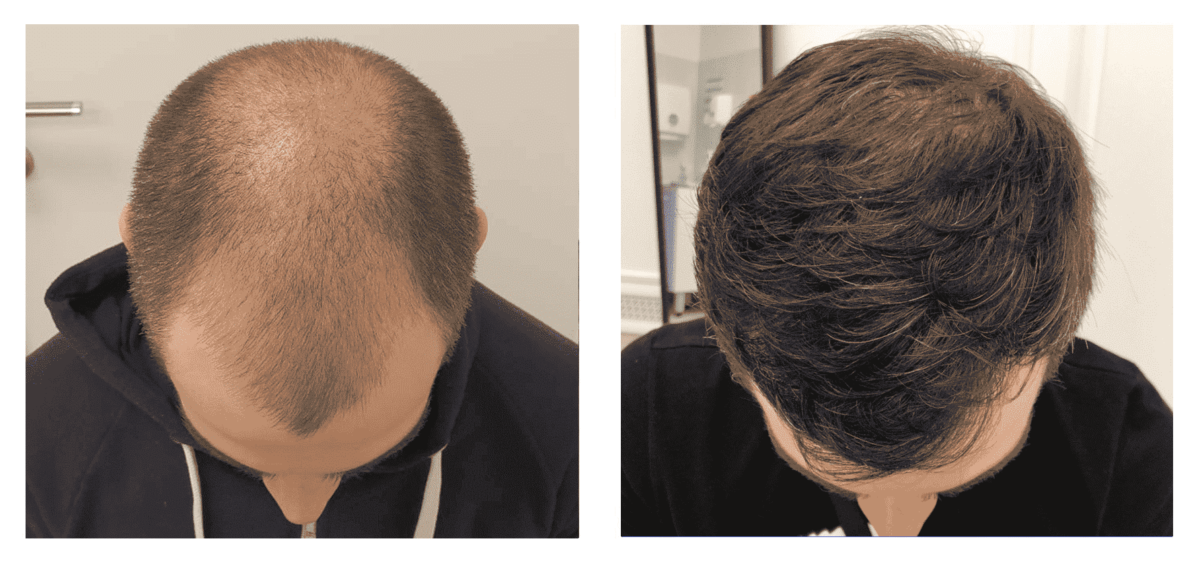
Hair transplantation has become a popular solution for individuals experiencing hair loss. Two primary techniques, Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), have emerged as the most commonly used methods. This article will delve into the intricacies of these techniques, comparing their processes, benefits, and drawbacks to help you make an informed decision. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on various factors, including the individual’s needs, the extent of hair loss, and personal preferences.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
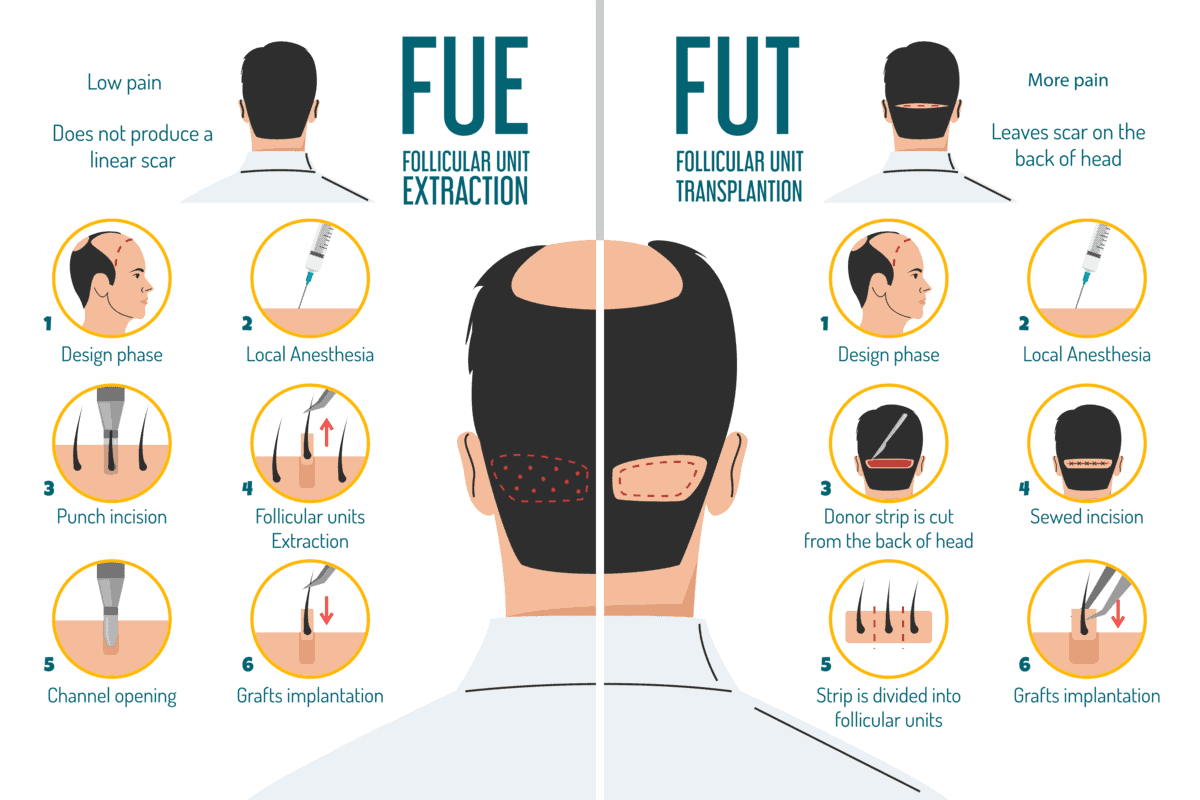
FUE is a minimally invasive hair transplant technique that involves the extraction of individual hair follicles from the donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) and their implantation into the recipient area. This method has gained popularity due to its less invasive nature and the absence of a linear scar.
The Procedure:
- Preparation: The donor and recipient areas are prepared, and local anaesthesia is administered to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Extraction: Using a specialized tool, small circular incisions are made around individual hair follicles, which are then extracted with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissue.
- Grafting: The extracted follicles are carefully prepared and then implanted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area.
Advantages:
- Minimally Invasive: No large incisions are made, resulting in a lower risk of scarring.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients typically experience a faster recovery time compared to FUT.
- Natural Results: FUE often provides a more natural-looking result with less visible scarring.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: FUE is generally more expensive due to the precision and time required.
- Time-Consuming: The extraction process can be time-consuming, particularly in cases of extensive hair loss.
- Graft Quality: There may be a higher risk of transection (damage) to follicles if not performed by an experienced surgeon.
An International Perspective:
In the United States, according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), FUE has become increasingly popular due to its minimally invasive nature, with many clinics adopting advanced techniques and tools. This is also so in Turkey, where Istanbul is renowned for its affordable FUE hair transplant clinics, attracting patients worldwide.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as strip harvesting, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and then implanting these units into the recipient area. This technique has been the traditional choice for hair transplantation.
The Procedure:
- Preparation: Local anaesthesia is administered to both the donor and recipient areas.
- Strip Removal: A strip of the scalp is surgically removed from the donor area, usually from the back of the head.
- Dissection: The strip is carefully dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope.
Grafting: The follicular units are implanted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area.
Advantages:
- Higher Yield: FUT can provide a larger number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for patients with extensive hair loss.
- Consistency: Often results in a higher percentage of viable grafts due to the meticulous dissection process.
Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than FUE due to the shorter time required for the procedure.
Disadvantages:
- Scarring: A linear scar is left in the donor area, which can be noticeable if the hair is cut very short.
- Longer Recovery: The recovery period is longer compared to FUE, with potential discomfort in the donor area.
Invasive: The procedure is more invasive, which can lead to more postoperative discomfort.
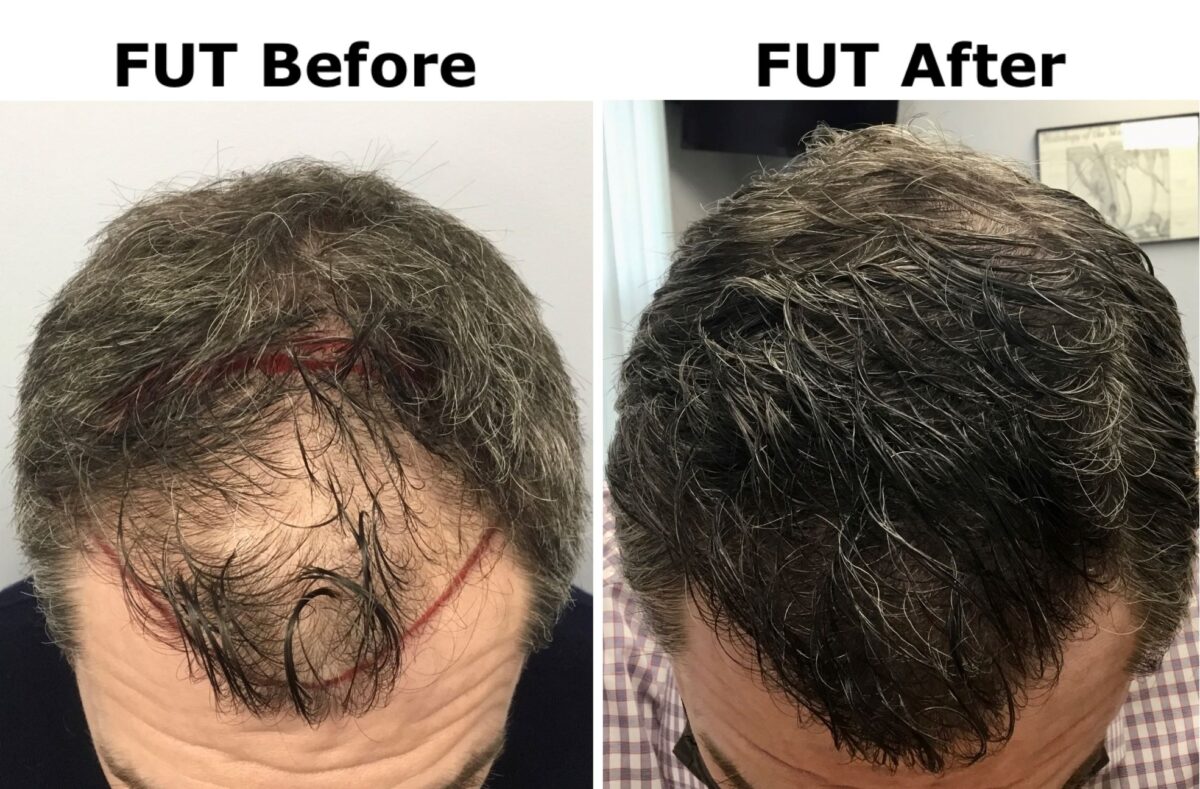
An International Perspective:
In India, hair transplant clinics in cities like Delhi and Mumbai often use FUT due to its cost-effectiveness and high graft yield. According to the Indian Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS), FUT remains a common choice for those seeking extensive coverage. The same is true in Brazil, where in São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, FUT is popular among patients who require a high number of grafts.
Recovery Time:
FUE: Recovery typically takes 7-10 days, with most patients resuming normal activities within a week whereas with FUT, recovery can take 10-14 days, with patients often needing more time off work due to the invasive nature of the procedure.
Patient Satisfaction:
With FUE, patient satisfaction is high due to the minimal scarring and faster recovery. Many patients appreciate the ability to wear shorter hairstyles without visible scars. In contrast, while FUT provides excellent results, some patients are concerned about the linear scar, which can be a factor in their overall satisfaction.
Making a decision:
Both FUE and FUT have proven to be effective methods for hair transplantation, each with its unique advantages and limitations. FUE is often preferred for its minimally invasive nature and faster recovery, making it ideal for patients seeking natural-looking results with minimal scarring. On the other hand, FUT remains a viable option for those who require a higher number of grafts and are comfortable with the possibility of a linear scar. Ultimately, the choice between FUE and FUT should be made in consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon, who can assess the patient’s specific needs and goals. By understanding the differences between these techniques, individuals can make informed decisions and achieve the best possible outcomes for their hair restoration journey.
